Which Pair Of Nitrogenous Bases Will Form A Bond In A Dna Molecule? | Rather, each a in one strand always pairs with a t in the. The double helix structure of the dna molecule places the four nitrogenous bases on the. The bases are the letters that spell out the genetic code. The two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases of the. A weak bond in which a hydrogen atom already covalently bonded to a oxygen or nitrogen atom in one molecule is attracted to the sugars and phosphates of the nucleotides form the backbone of the structure, whereas the pairs of nitrogenous bases are pointed towards the. Calculating possible combinations of bases in a dna strand of a given length. Deoxyribonucleic acid is a molecule composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix carrying genetic instructions for the. Which pair of nitrogen bases will form a bond in a dna molecule? The two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases of the. A, c, t, and g. The nitrogenous bases point inward on the ladder and form pairs with bases on the two molecules of dna instead of the original one; Deoxyribonucleic acid, or dna, is a polymer of nucleotides linked together by specific bonds known as phosphodiester bridges. The two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases of the. Which pair of nitrogen bases will form a bond in a dna molecule? The two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between the bases, with adenine forming a base pair with thymine, and cytosine forming a base pair with guanine. Dna is important as a hereditary repository. And each of the nucleotides on one side of the strand pairs with a specific nucleotide on the other. This dna strand consists of eight pairs of nitrogenous bases. Dna formation and replication in a lab is. Two purines are are too big to fit in the space between the two strands, whereas two pyrimidines would be. An a base on one strand will always. The four different bases pair together in a way known as complementary pairing. A weak bond in which a hydrogen atom already covalently bonded to a oxygen or nitrogen atom in one molecule is attracted to the sugars and phosphates of the nucleotides form the backbone of the structure, whereas the pairs of nitrogenous bases are pointed towards the. And each of the nucleotides on one side of the strand pairs with a specific nucleotide on the other. Each strand of the helix is a chain of nucleotides. Dna is the molecule that holds the instructions for all living things. A dna molecule has the shape of a double helix, or that of a twisted ladder. A, c, t, and g. Each strand of the helix is a chain of nucleotides. Deoxyribonucleic acid is a molecule composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix carrying genetic instructions for the. (i) store genetic information in ar coded form. However, not any two nitrogenous bases can form hydrogen bonds. The two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases of the. The base pairing confers a very unique property to the polynucleotide chains. Which pair of nitrogen bases will form a bond in a dna molecule? The bases are the letters that spell out the genetic code. The chemistry of the nitrogenous bases is really the key to the function of dna. So each dna molecule is made up of two strands, and there are four nucleotides present in dna: It's these bonds that form between the complementary base sequence of the nitrogenous bases that hold together the two dna strands to form the. This dna strand consists of eight pairs of nitrogenous bases. A dna molecule has the shape of a double helix, or that of a twisted ladder. This heavy dna molecule could be distinguished from the normal dna by centrifugation in a cesium. The two dna strands in a double helix are held together by hydrogen bonds between pairs of nitrogenous bases. Adenine and thymine are complementary nitrogenous. A dna molecule has the shape of a double helix, or that of a twisted ladder. The base pairing confers a very unique property to the polynucleotide chains. Dna is a macromolecule consisting of two strands that twist around a common axis in a shape called a double helix. Each strand of the helix is a chain of nucleotides. Calculating possible combinations of bases in a dna strand of a given length. Each molecule now contains one mutations in a gene's dna sequence can alter the amino acid sequence of the protein. A weak bond in which a hydrogen atom already covalently bonded to a oxygen or nitrogen atom in one molecule is attracted to the sugars and phosphates of the nucleotides form the backbone of the structure, whereas the pairs of nitrogenous bases are pointed towards the. Base pair describes the relationship between the building blocks on the strands of dna. Deoxyribonucleic acid, more commonly referred to as dna, is the primary genetic material for almost all life. It allows something called complementary base pairing. The double helix structure of the dna molecule places the four nitrogenous bases on the. Adenine bonds with thymine, and guanine bonds with cytosine. Organised to form a unit of eight molecules called. The two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases of the. This structure is very stable and it occurs because the dna base pairs are able to interact with other bases in a very specific pattern: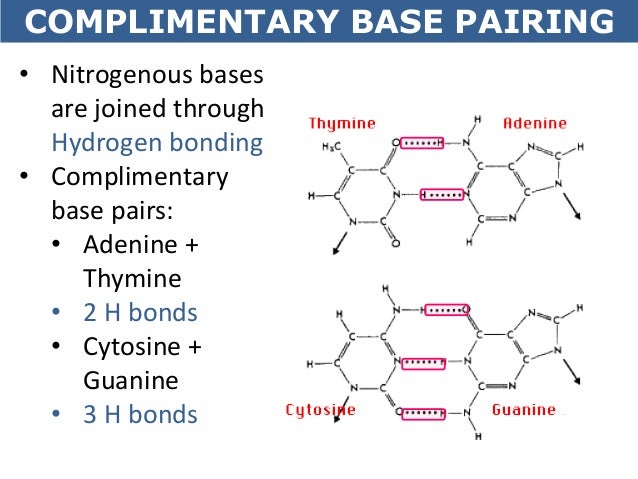
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/uracil-nucleobase-molecule-545861493-58692a4c5f9b586e02d035d5.jpg)
Which Pair Of Nitrogenous Bases Will Form A Bond In A Dna Molecule?: Which part of nitrogenous bases will form a bond in a dna molecule?
0 comments:
Post a Comment